These devices are precision timing circuits capable of producing accurate time delays or oscillations. In the time-delay or mono-stable mode of operation, the timed interval is controlled by a single external resistor and capacitor network. In the a-stable mode of operation, the frequency and duty cycle can be controlled independently with two external resistors and a single external capacitor.
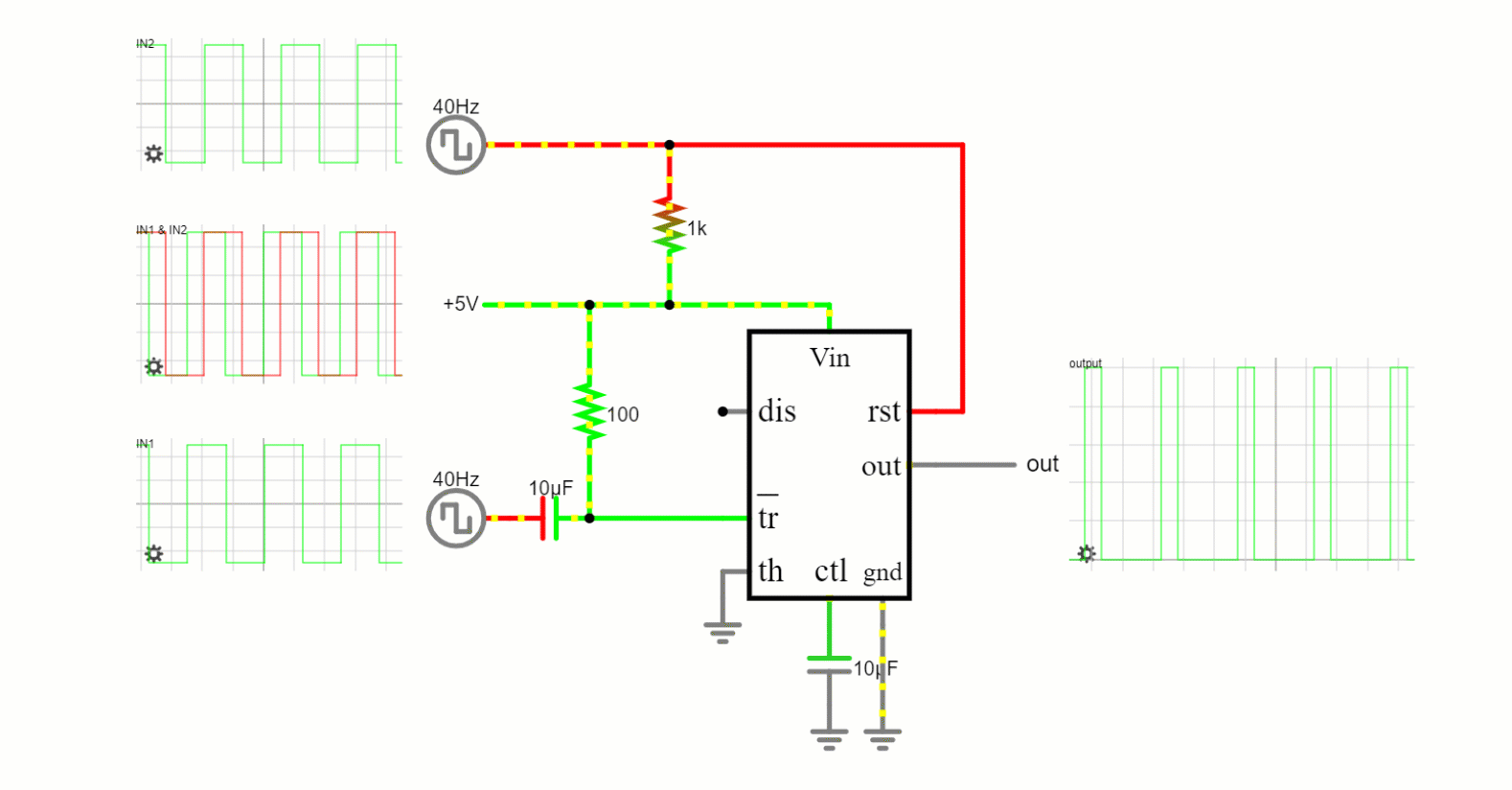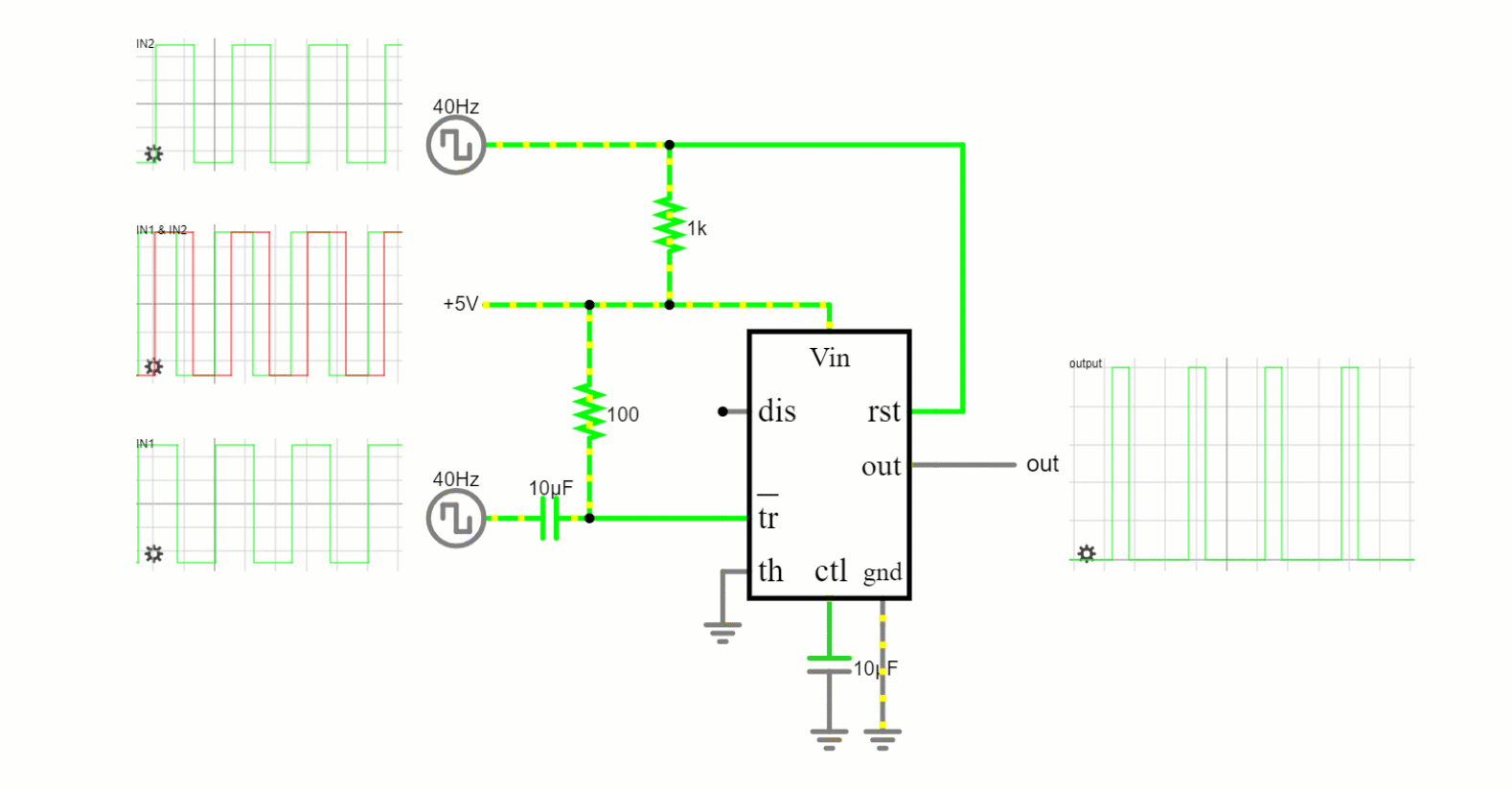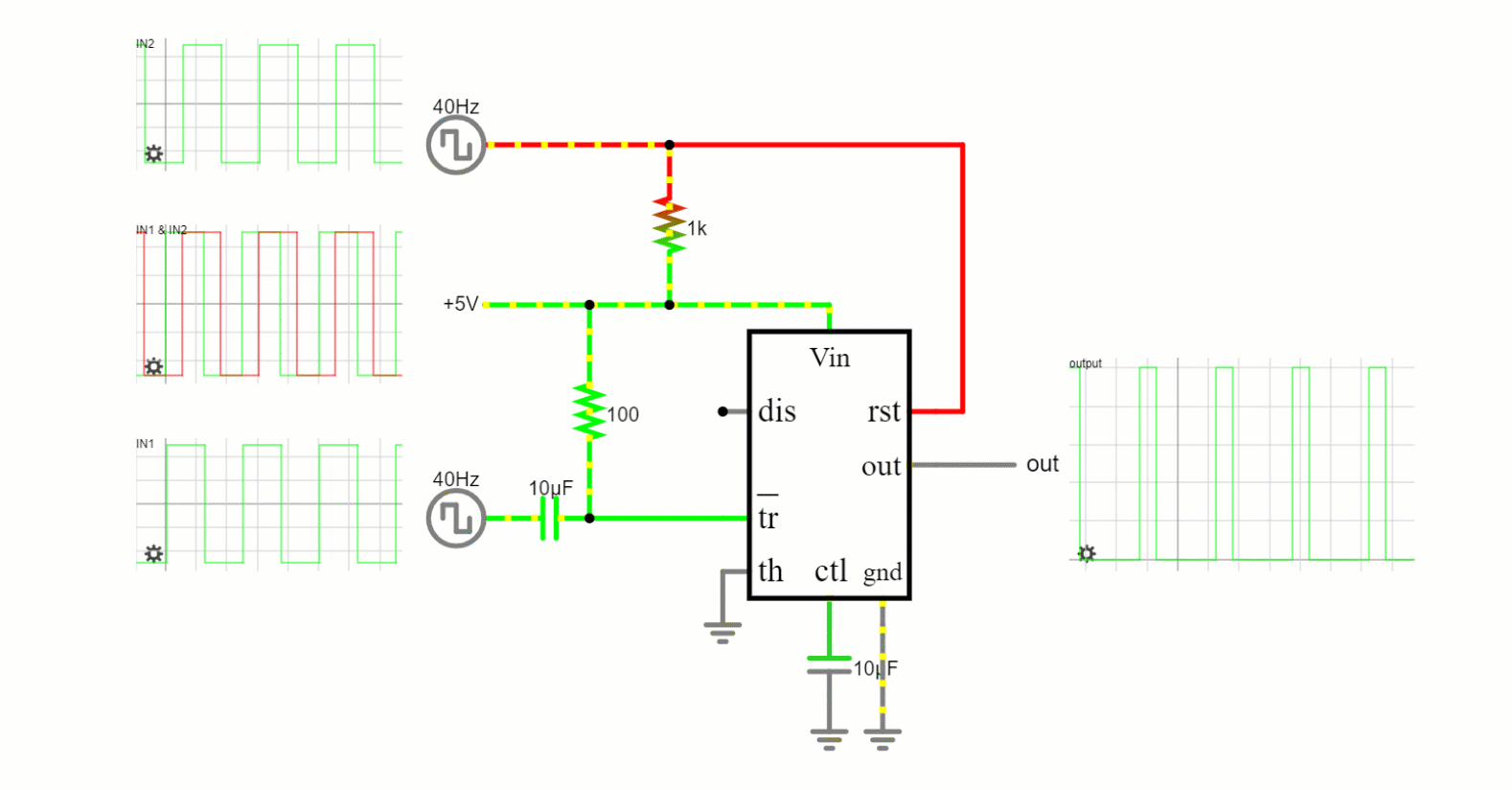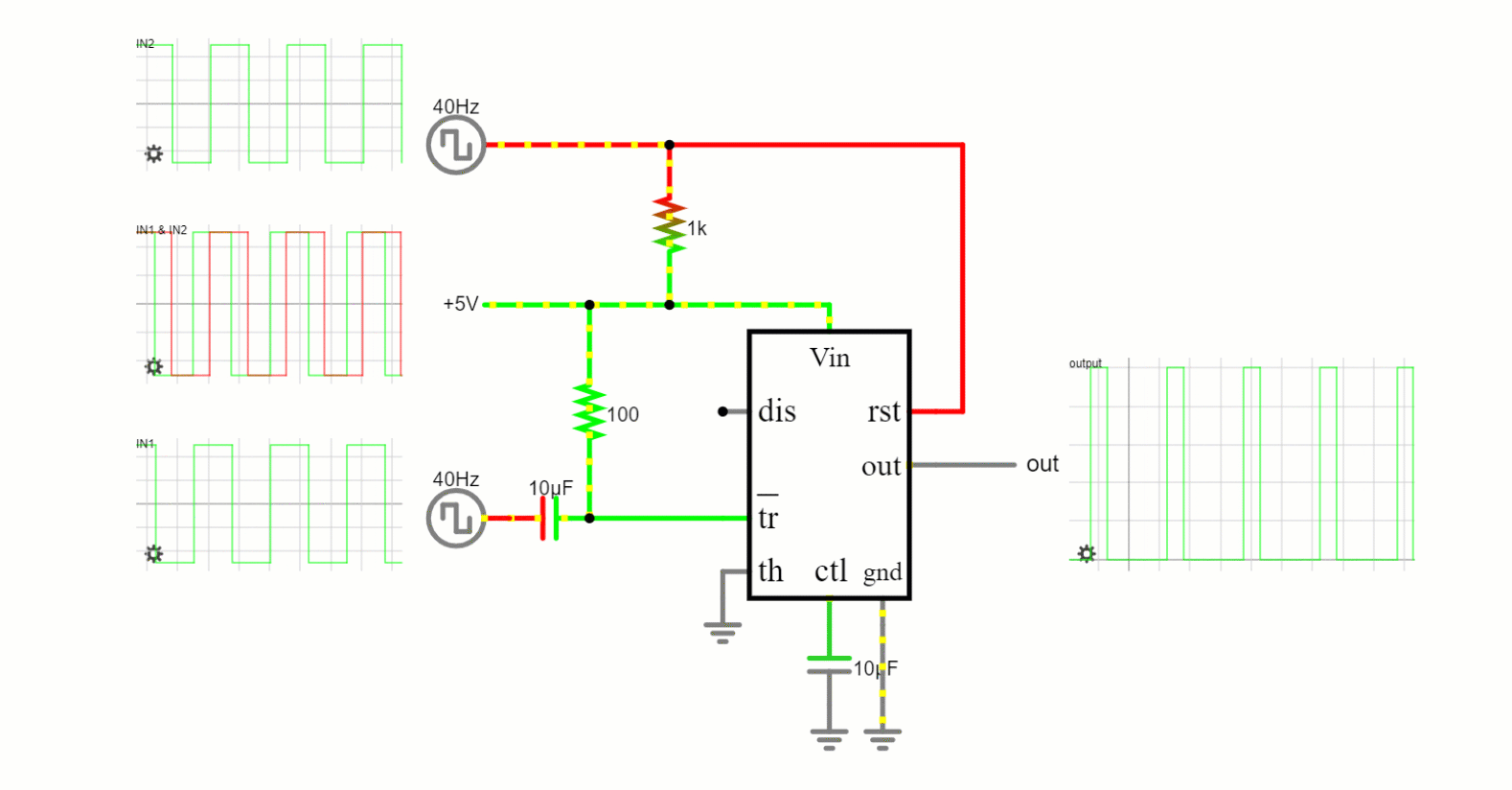
The threshold and trigger levels normally are two-thirds and one-third, respectively, of V CC. These levels can be altered by use of the control-voltage terminal. When the trigger input falls below the trigger level, the flip-flop is set, and the output goes high. If the trigger input is above the trigger level and the threshold input is above the threshold level, the flip-flop is reset and the output is low. The reset (RESET) input can override all other inputs and can be used to initiate a new timing cycle. When RESET goes low, the flip-flop is reset, and the output goes low. When the output is low, a low-impedance path is provided between discharge (DISCH) and ground.
The output circuit is capable of sinking or sourcing current up to 200 mA. Operation is specified for supplies of 5 V to 15 V. With a 5-V supply, output levels are compatible with TTL inputs.

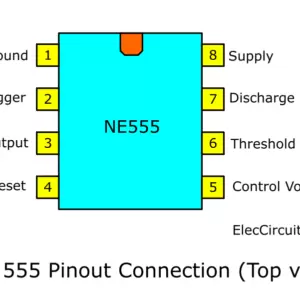
- Ground (GND): This is the reference voltage against which all other voltages are measured. It connects to the circuit’s ground or the negative terminal of the power supply.
- Trigger (TRIG): When a voltage on this pin drops below half of the control voltage (typically 1/3 of the VCC if the control voltage is not externally defined), the output becomes high and the timer activates.
- Output (OUT): This pin can either source or sink current. It’s the main output of the timer. Depending on the mode of the 555 timer, the output pin might produce a continuous square wave (Astable mode) or a single pulse width (Monostable mode).
- Reset (RESET): When a negative pulse is applied to this pin, the timer resets and the output goes low. If the reset functionality isn’t required in a circuit, this pin is typically connected to VCC to prevent unintended resets.
- Control Voltage (CV): An external voltage applied to this pin can be used to modulate the threshold and trigger levels. If not being used for modulation, a small ceramic capacitor (like 0.01μF) is typically connected to ground to filter noise.
- Threshold (THRESH): Compares the voltage applied to it to a reference voltage (usually 2/3 VCC). In many timer circuits, this pin is directly connected to the external capacitor that dictates the timing of the circuit.
- Discharge (DISCH): Connected internally to an NPN transistor, this pin is primarily used to discharge the external timing capacitor.
- VCC: This pin powers the 555 timer and can typically accept voltages between 4.5V and 15V.
Features:-
- Timing From Microseconds to Hours
- Astable or Monostable Operation
- Adjustable Duty Cycle
- TTL-Compatible Output Can Sink or Source Up to 200 mA
Specifications:-
| Product Attribute | Attribute Value |
| Series: | NE555 |
| Type: | Standard |
| Number of Internal Timers: | 1 Timer |
| Supply Voltage – Max: | 16 V |
| Supply Voltage – Min: | 4.5 V |
| Minimum Operating Temperature: | 0 C |
| Maximum Operating Temperature: | + 70 C |
| Mounting Style: | SMD/SMT |
| Package/Case: | SOIC-8 |
| High-Level Output Current: | 200 mA |
| Low-Level Output Current: | – 200 mA |
| Operating Supply Current: | 2 mA |
| Subcategory: | Clock & Timer ICs |
Overall Operation
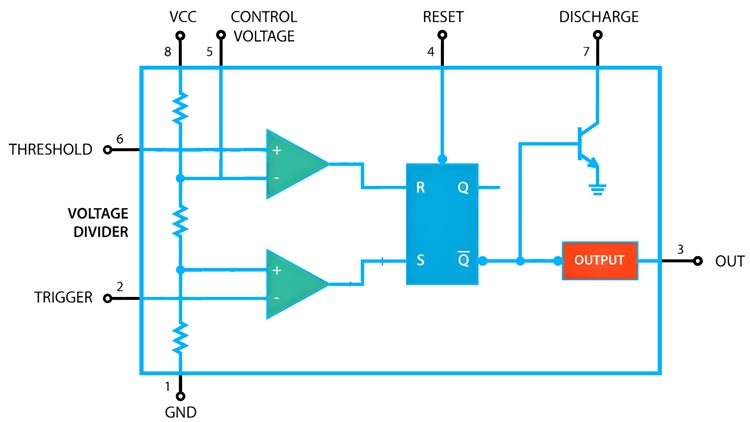
Internally, the 555 chips layout can be visualized as a block diagram featuring 2 comparators, a flip-flop, a voltage divider, a discharge transistor, and an output stage. This voltage divider, in particular, comprises three 5k resistors, setting two reference voltages at 1/3 and 2/3 of the supplied voltage (which varies between 5 and 15V). Comparators within the 555 Timer act as voltage comparison units; their function is to compare analog inputs and produce outputs accordingly. The interaction between the “Trigger,” “Threshold,” and “Control” pins directly influences the comparators’ output. This output is channeled into a flip-flop, which toggles based on the input conditions and can be overridden using an external “Reset” pin. Concluding the internal setup, the flip-flop’s output feeds into drivers capable of managing up to 200mA and a transistor connecting the “Discharge” pin to the ground.
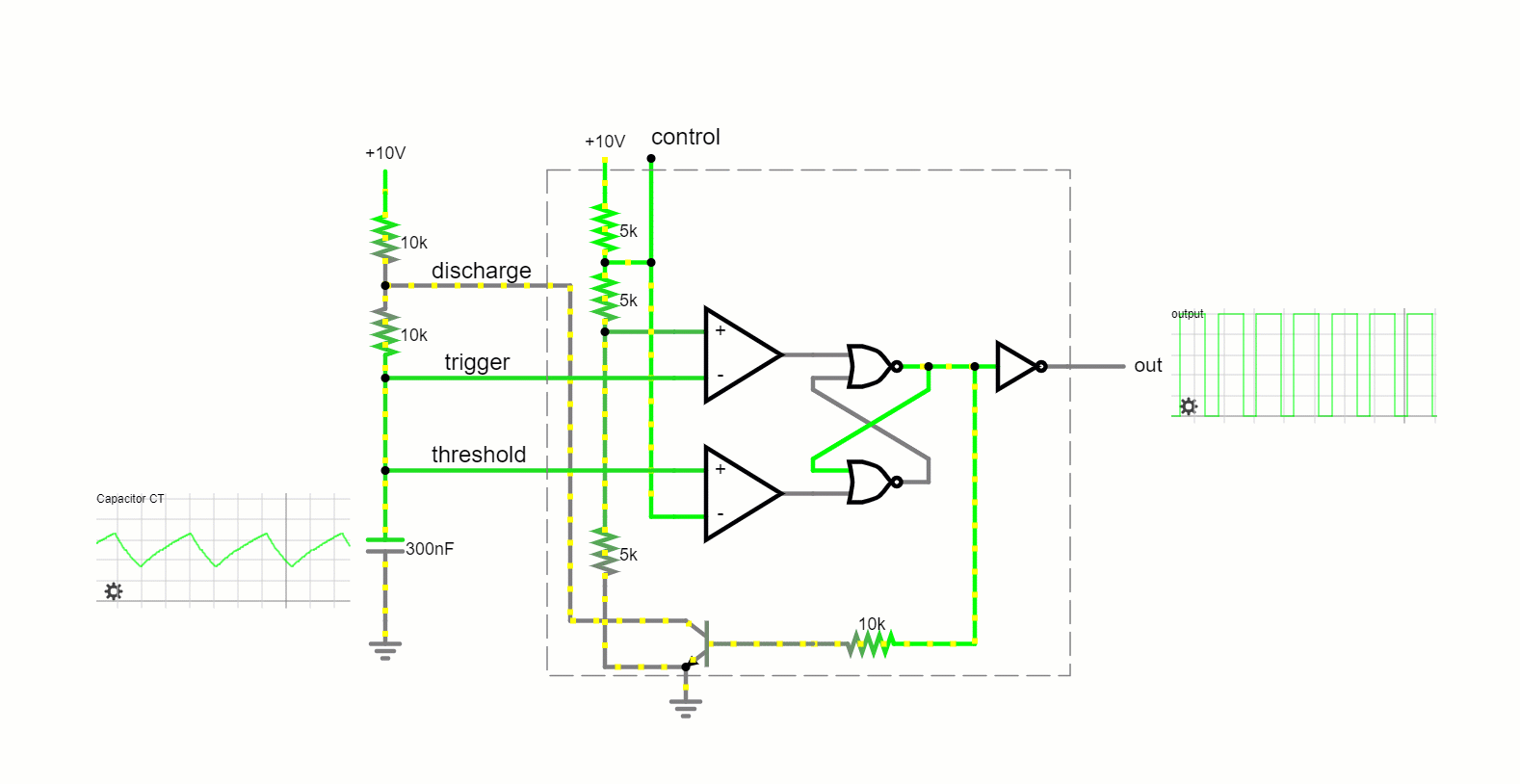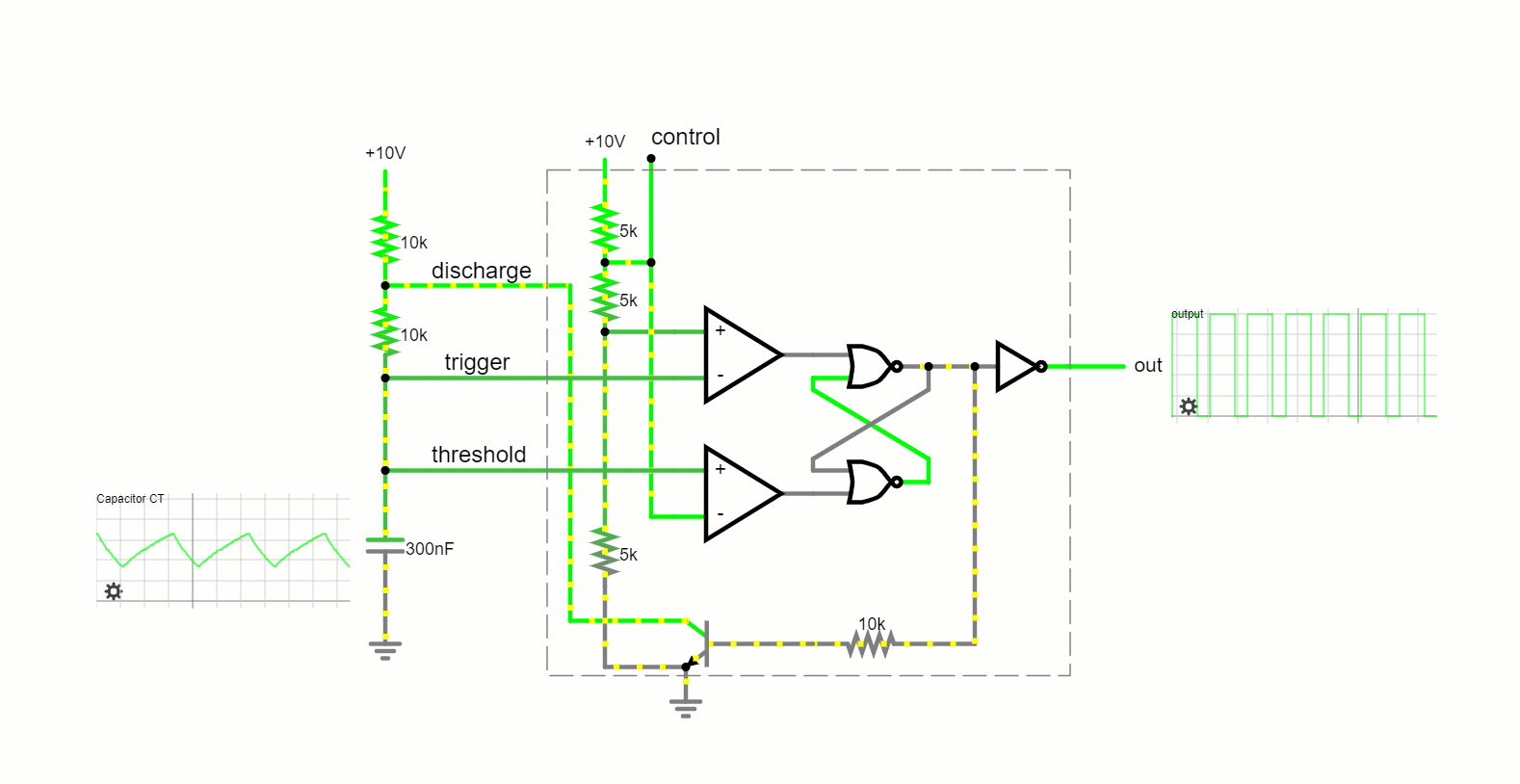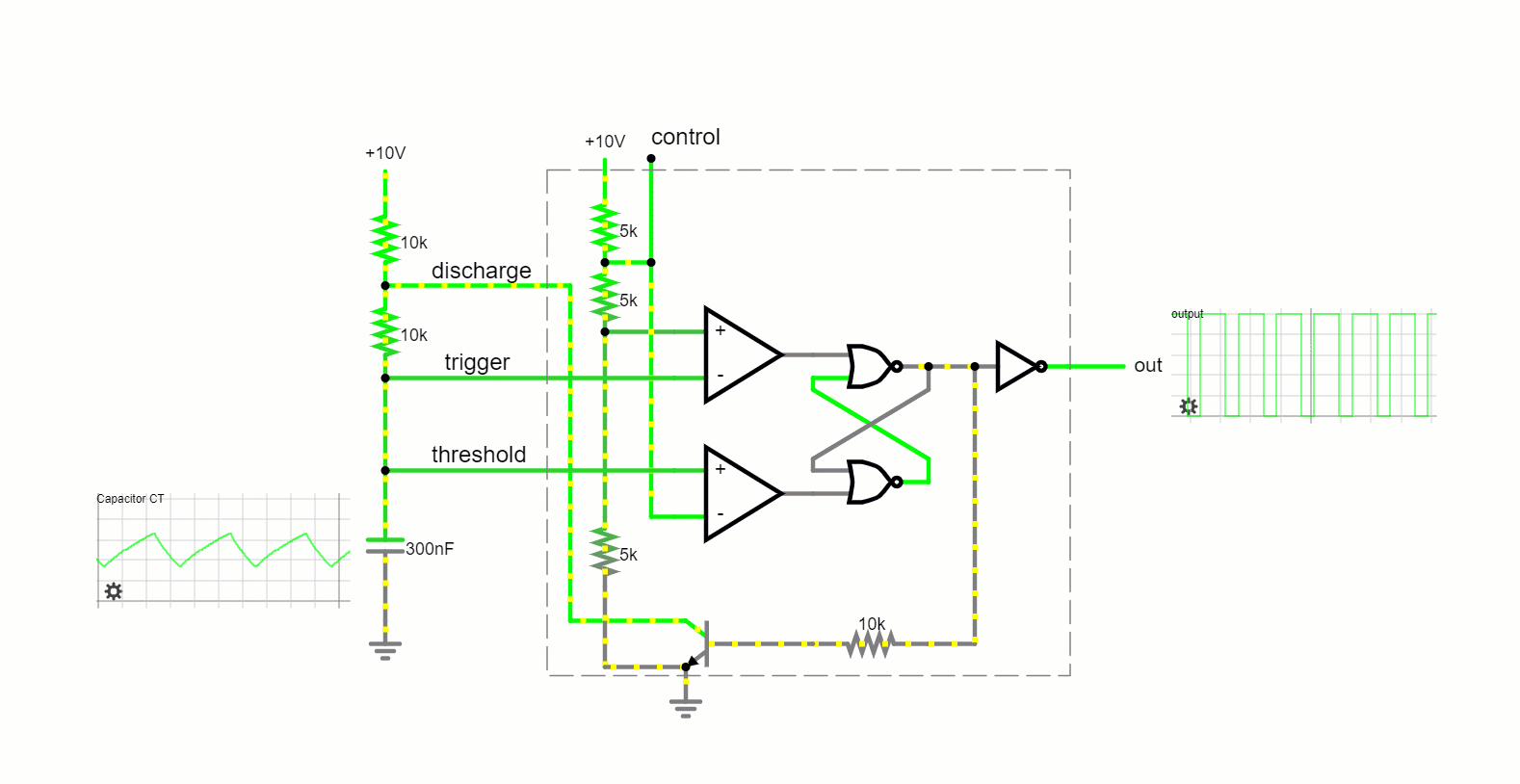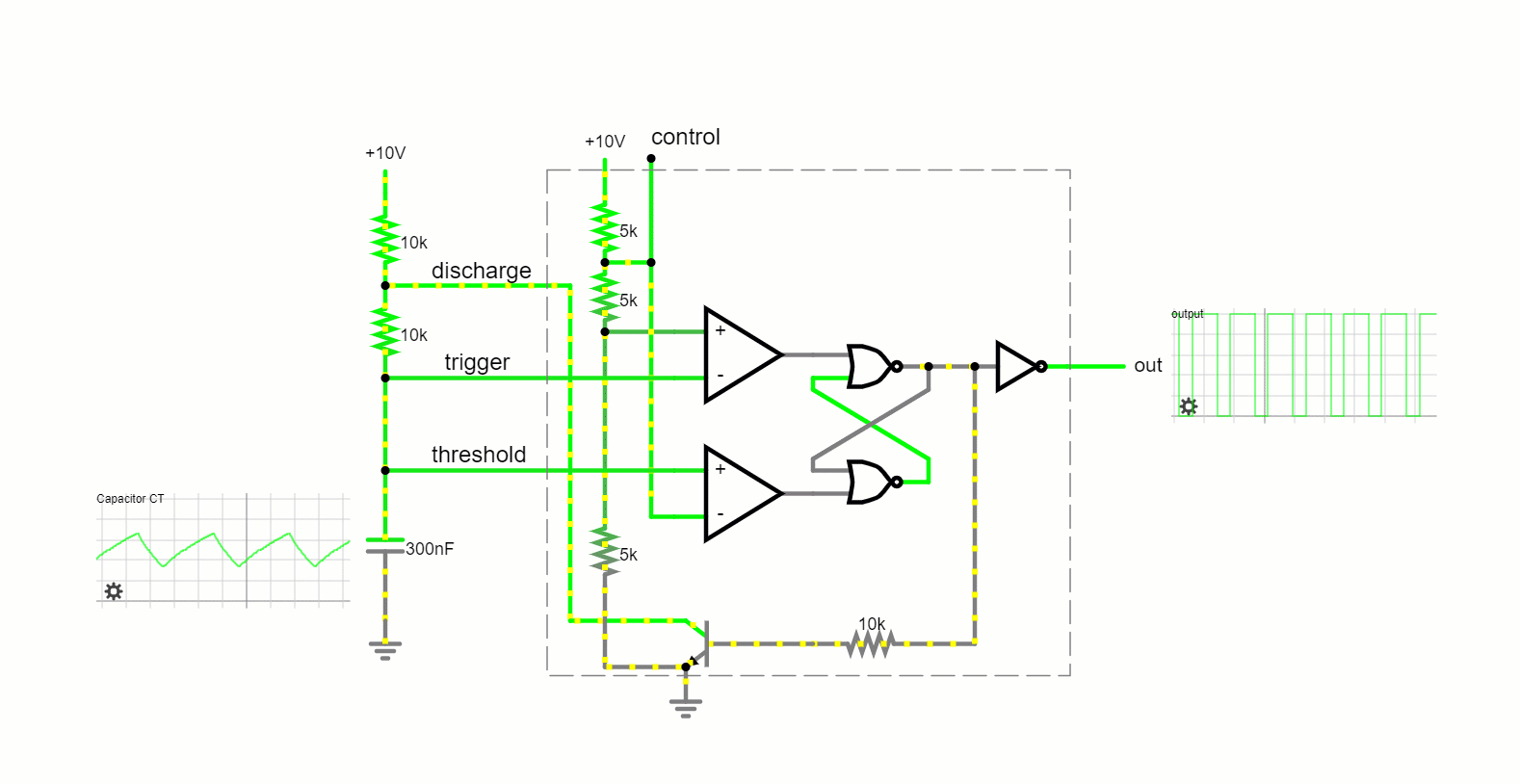
Operating Modes
Astable Mode:
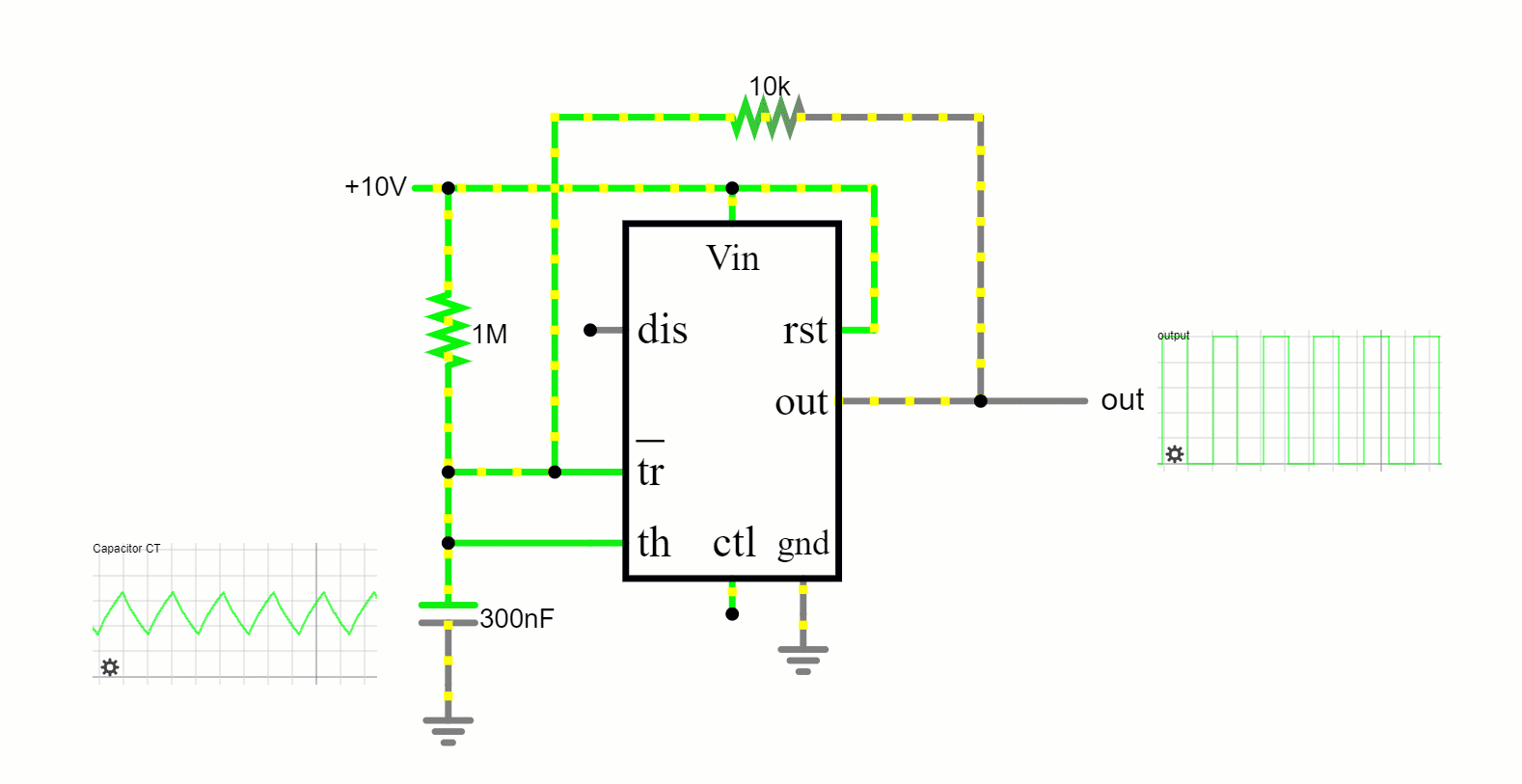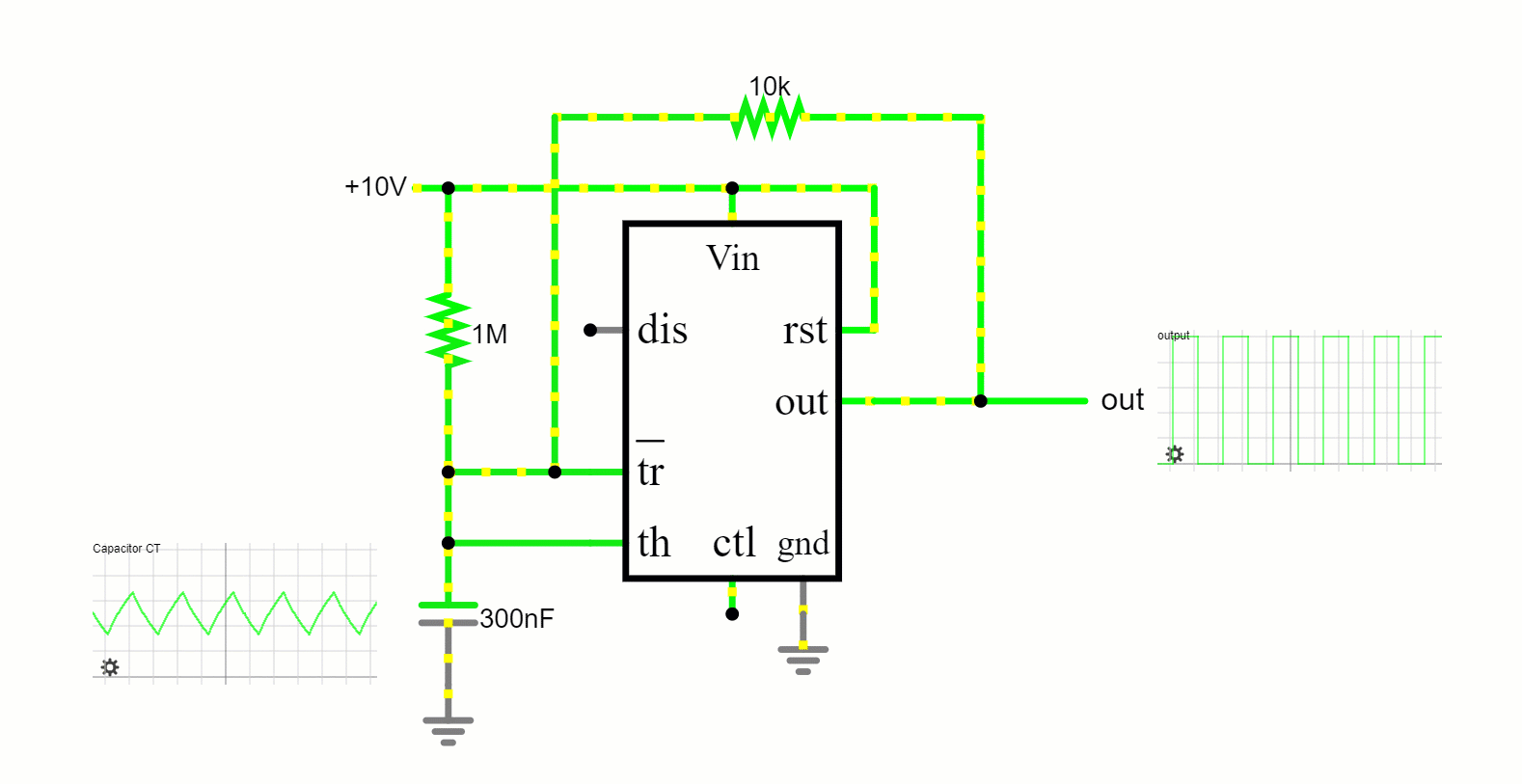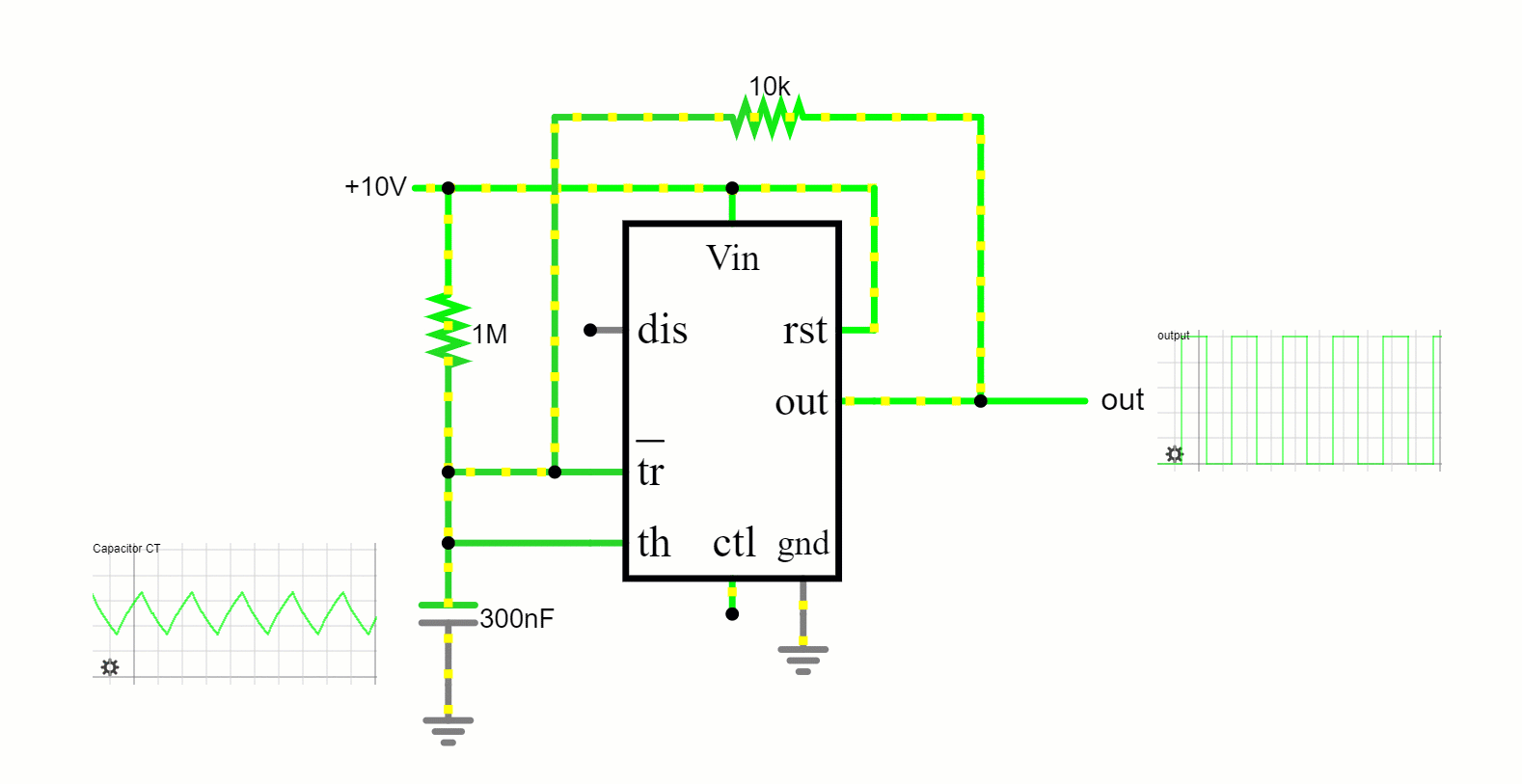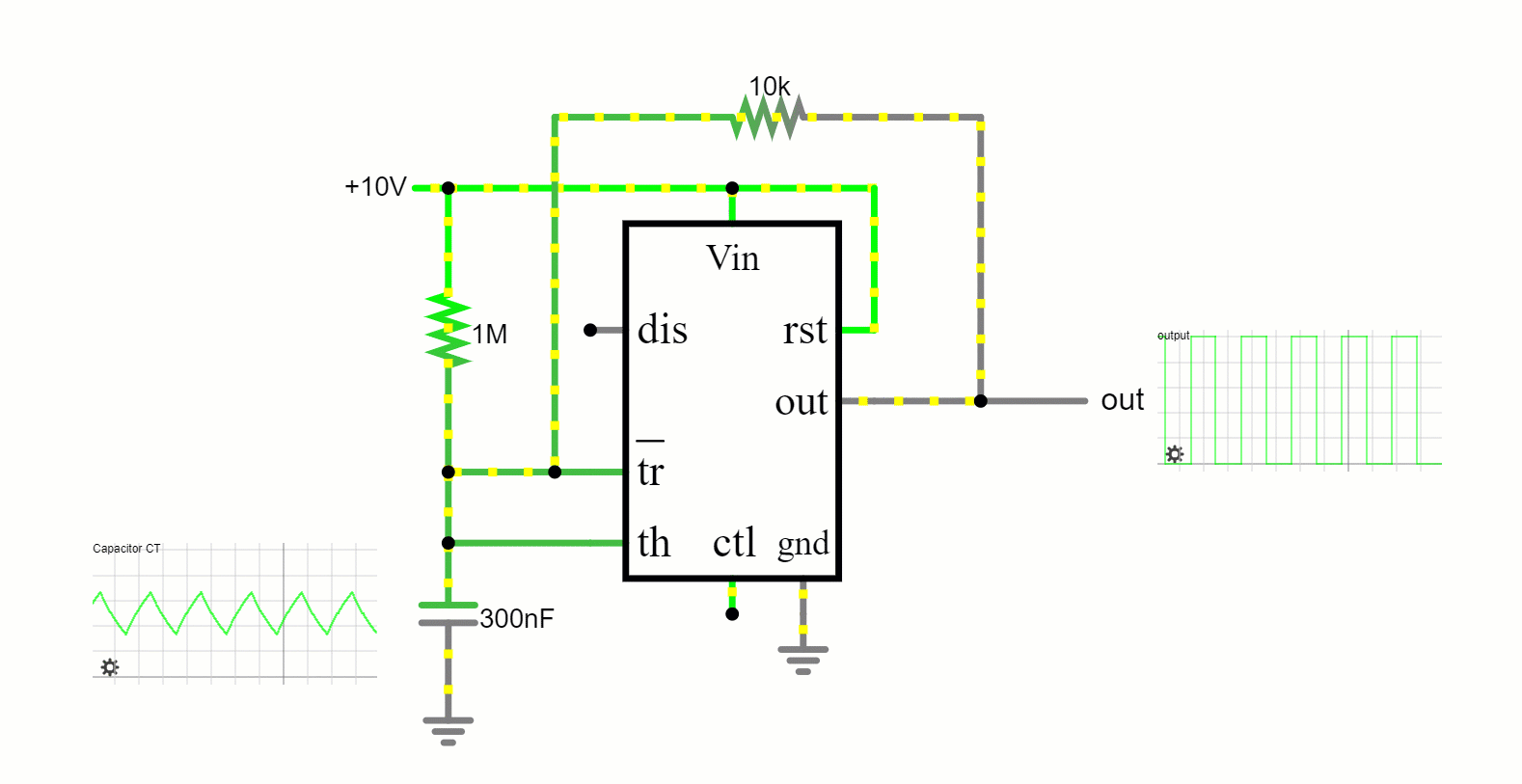
In this free-running mode, the 555 timer oscillates endlessly, transitioning between its high and low states, producing a continuous square wave output. This makes it apt for applications like tone generation and LED blinking.
Monostable Mode
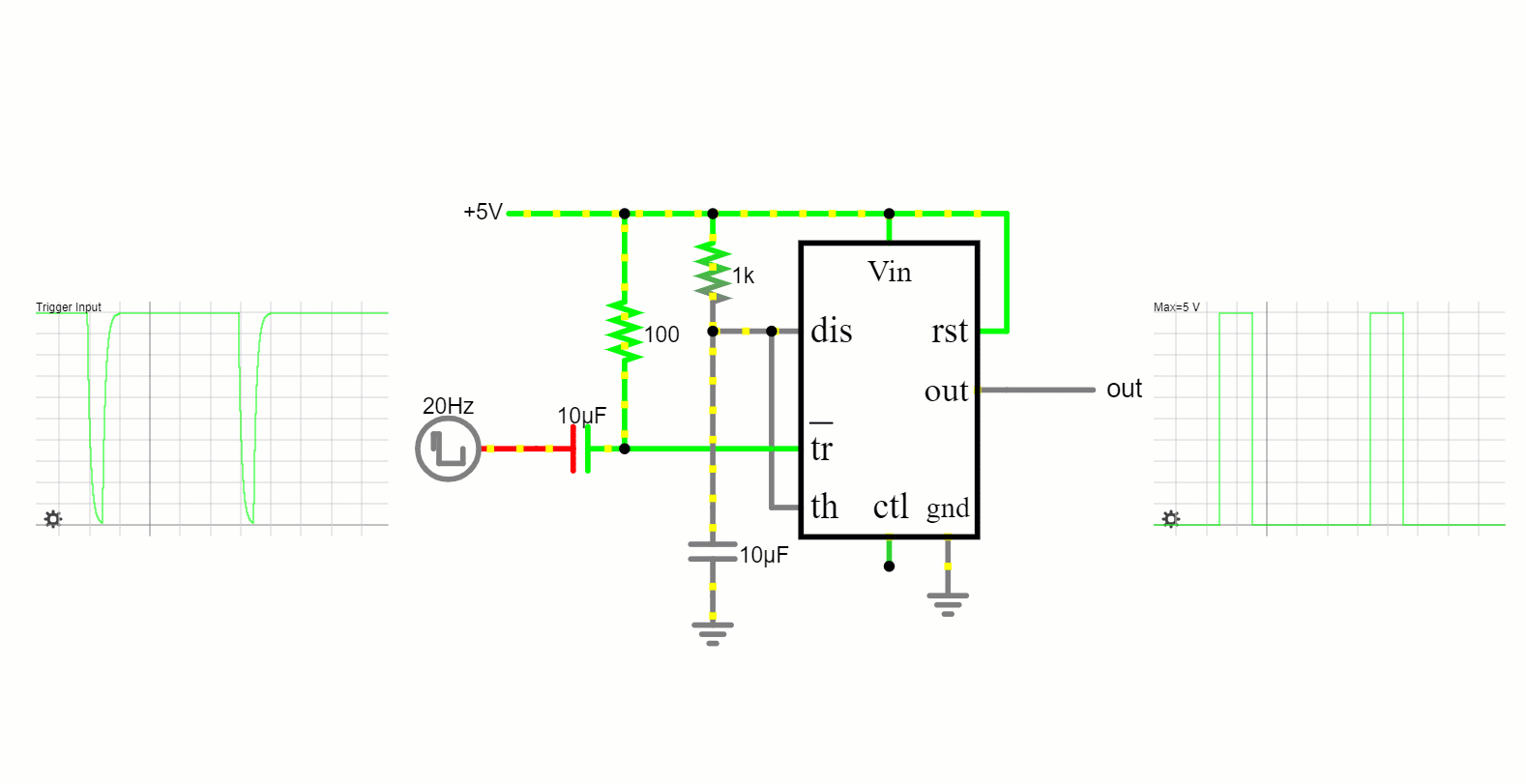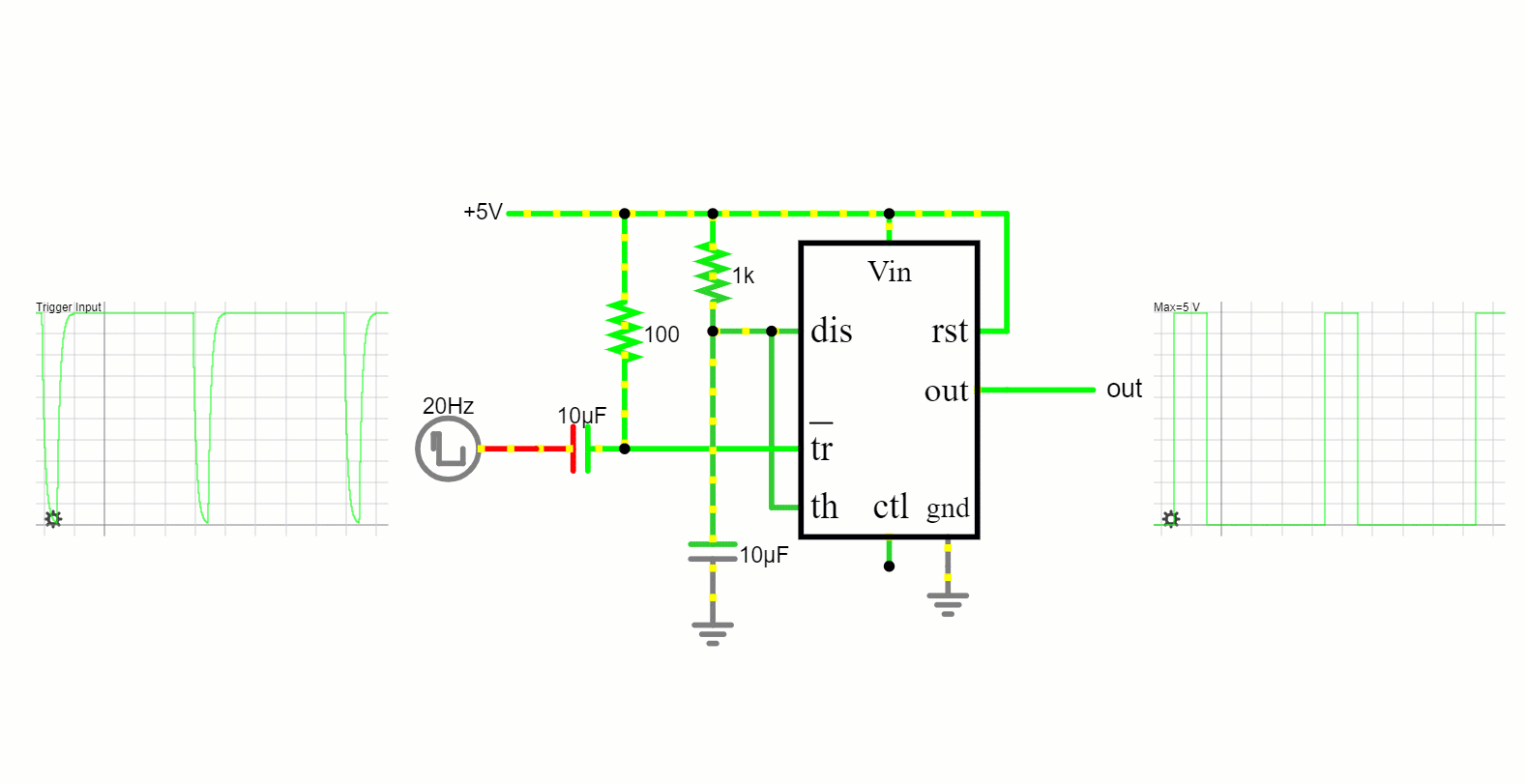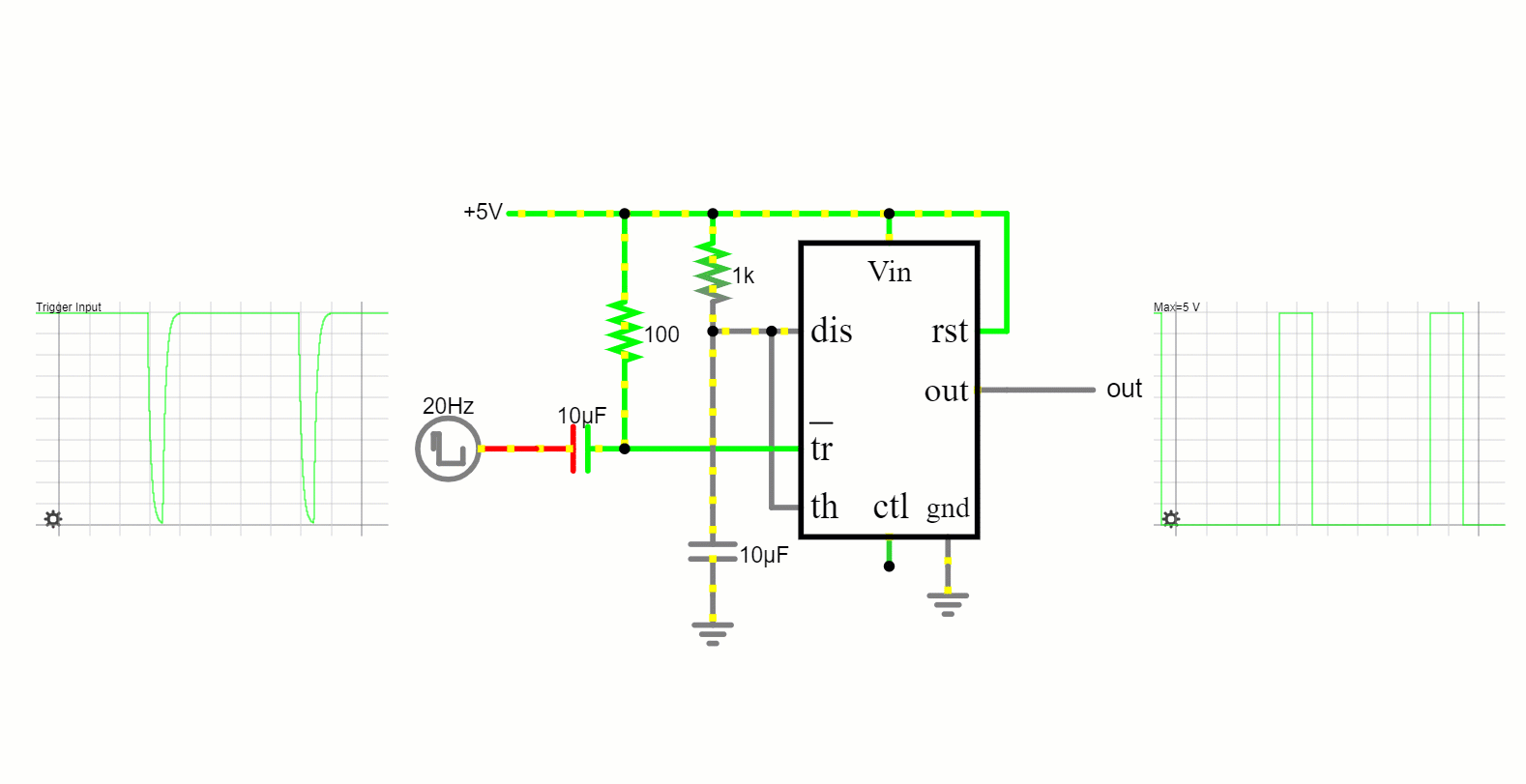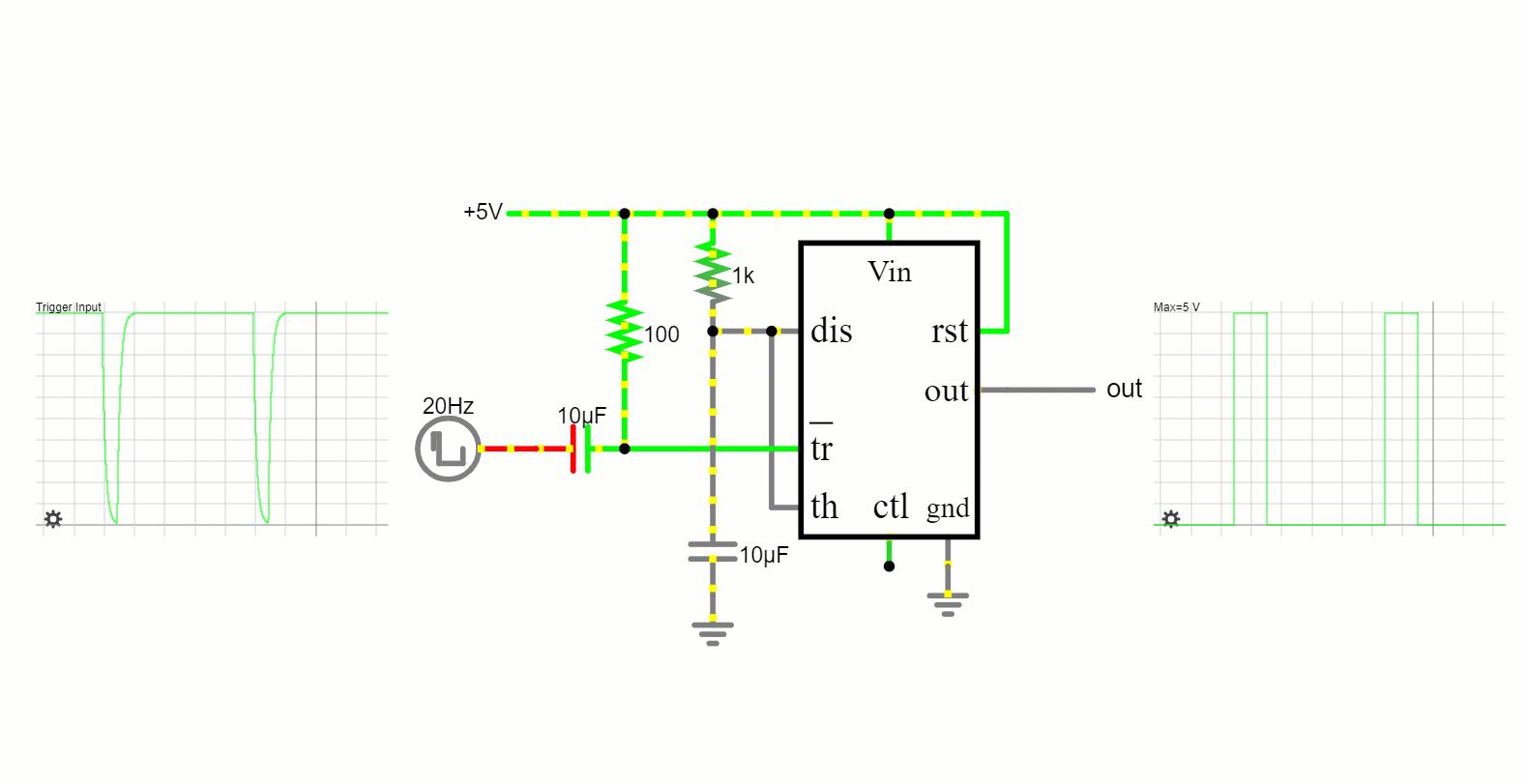
The 555 timer in this mode functions as a one-shot timer. It remains in its low state until triggered, after which it produces a high pulse for a defined period and then reverts to its low state.
Bistable Mode
This mode transforms the 555 timer into a basic flip-flop, a digital memory device. It has two stable states (high and low) and can maintain either until externally altered.
The 555 timer’s lasting popularity is a testament to its remarkable versatility. From simple hobby projects to sophisticated industrial applications, its presence is ubiquitous in the electronics world. Understanding its inner workings and functionalities is not only beneficial for electronic hobbyists but also instrumental for professionals aiming for adept circuit designs.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.